
Ultimate Guide to Cloud Cost Optimization
1. Infra-Level Optimization & Well-Architected Review (WAR) Key Strategies:
- Infra-Level Optimization & Well-Architected Review (WAR)
Key Strategies:
Well-Architected Review helps cloud architects build secure, high-performing, resilient, and efficient infrastructure for a variety of applications and workloads. Built around six pillars—operational excellence, security, reliability, performance efficiency, cost optimization, and sustainability—WAR provides a consistent approach for customers and partners to evaluate architectures and implement scalable designs.
Well-Architected Six Pillars
- Security Pillar
The security pillar describes how to take advantage of cloud technologies to protect data, systems, and assets in a way that can improve your security posture. This paper provides in-depth, best-practice guidance for architecting secure workloads on cloud.
- The Reliability pillar
Reliability pillar encompasses the ability of a workload to perform its intended function correctly and consistently when it’s expected to. This includes the ability to operate and test the workload through its total lifecycle. This paper provides in-depth, best practice guidance for implementing reliable workloads on cloud.
- The performance efficiency
performance efficiency pillar includes the ability to use cloud resources efficiently to meet performance requirements, and to maintain that efficiency as demand changes and technologies evolve.
- Cost optimization
Cost optimization is a continual process of refinement and improvement over the span of a workload’s lifecycle. The practices in this paper help you build and operate cost-aware workloads that achieve business outcomes while minimizing costs and allowing your organization to maximize its return on investment.
- Sustainability
Sustainability addresses the long-term environmental, economic, and societal impact of your business activities. When building cloud workloads, the practice of sustainability is understanding the impacts of the services used, quantifying impacts through the entire workload lifecycle, and applying design principles and best practices to reduce these impacts.
For detailed Info use the below links
AWS: https://aws.amazon.com/architecture/well-architected/?ams%23interactive-card-vertical%23pattern-data-1930237524.filter=%257B%2522filters%2522%253A%255B%255D%257D&ams%23interactive-card-vertical%23pattern-data-1930237525.filter=%257B%2522filters%2522%253A%255B%255D%257D
Azure: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/well-architected/
2. Modernization & Automation
As organizations move towards modernizing their workloads in the cloud, there are key capabilities that need to be in place to enable the success of the modernization journey. The capabilities include organization structure, modernization strategy, automation, team readiness, and stakeholder sponsorship. Out of these, automation plays an outsized role in realizing the benefits of modernization, especially in terms of agility, scalability, and operational efficiency.
But first, “automation” can mean a lot of things to a lot of people. In this post, automation refers to the tools and processes that use code and configuration to replace manual steps to achieve a particular outcome.
Automation objectives during the initiation phase
The initiation phase of a modernization program is generally focused on defining business objectives, scope, budget, organization structure, and testing strategy. Automation strategy is often overlooked and not included in the initiation phase, as it is considered more of a tactical activity than a strategic planning component. As a result, automation becomes an afterthought during the planning and implementation phases, leading to automation not receiving the required attention within the larger context of the modernization strategy.
Automation strategy should be a key deliverable of the initiation phase of any modernization program, with clear automation objectives defined and mapped against program objectives. During the planning phase, expand the automation strategy to include the automation approach, budget, and implementation plan (including design, development, testing, deployment, and operations). Automation planning should be a parallel track to modernization planning (as illustrated in Figure 1), with key interdependencies built in against critical milestones.
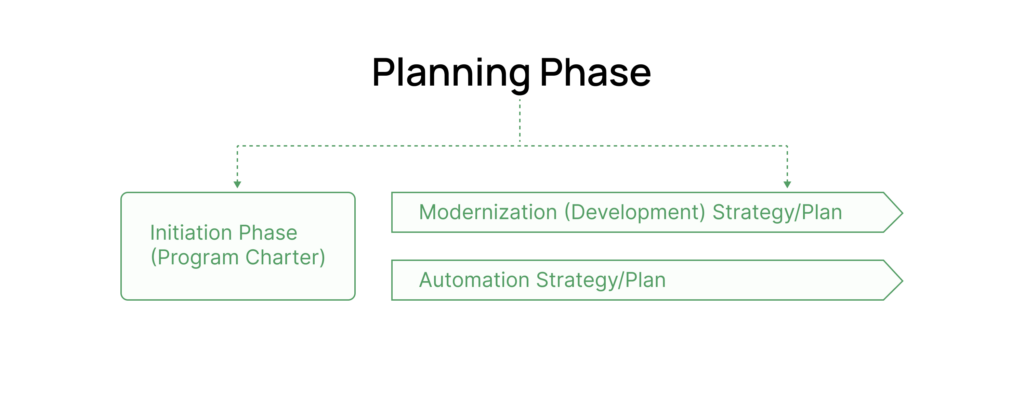
Figure 1: Deliverables of Planning Phase
Operating model
The mandate for application development teams is to focus on quickly delivering business functionality; however, automation is not always a priority. Consider creating a separate team whose primary focus is building automation capabilities that accelerate the development lifecycle. The automation and development teams will operate as interdependent functions that align with the overall program timeline to achieve a common business objective.
The organizational Agile and DevOps practices should promote cross-functional collaboration between the development and automation agile teams with a shared ownership of modernization deliverables throughout the development lifecycle, as shown in Figure 2. This approach fosters faster feedback loops, continuous integration, and emphasizes modernization outcomes as a shared responsibility among team members.
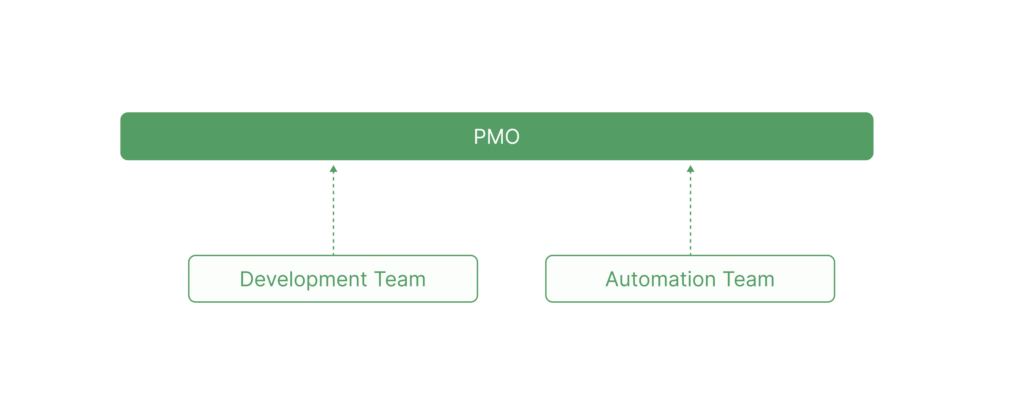
Figure 2: Team structure
Segregated duties between the development and automation teams prevents conflict of interest and reduces the possibility of teams performing tasks outside of the defined automated process. It is crucial to establish clear policies, communicate expectations, and regularly review and update access controls. As a general guideline, all environment builds, deployments, configurations, and data loads should be performed via automated processes.
There are two ways to organize automation teams. 1/ Shared teams: In this approach, a centralized automation team caters to automation needs across the organization. This approach is followed when the organization has a central DevOps strategy. It includes centralized deployment pipelines with a unified set of automation tools and processes. 2/ Dedicated teams: In this approach, a dedicated automation team is formed to build out automation for a specific modernization initiative or program. This team is eventually merged into a central DevOps team after the completion of program-specific automation deliverables.
Automation strategy – end to end automation
Organizations need to look at defining their automation strategy from an end-to-end perspective across the development lifecycle. Build the automation toolchain (which includes tools and processes) across the software lifecycle. The toolchain should include environment builds, development, version control, continuous integration, code quality, continuous deployment, containerization, monitoring, collaboration, and testing.
Automation in cloud security is critical, as it addresses challenges posed by the dynamic nature of cloud environments. Automation helps maintain security and compliance with speed and scale by proactively identifying and resolving security gaps, patch management, threat detection, and incident response.
Create an automated observability solution that helps teams monitor and optimize the performance, reliability, and security of their applications and infrastructure without the need for elevated access. This provides teams with visibility into each environment, enabling them to mitigate issues through proactive monitoring and improving operational efficiency.
Selecting the right combination of tools is important for building an efficient and effective workflow. The tools selected for the toolchain should have good interoperability with each other and function as an integrated unit throughout the lifecycle. Figure 3 shows a sample toolchain
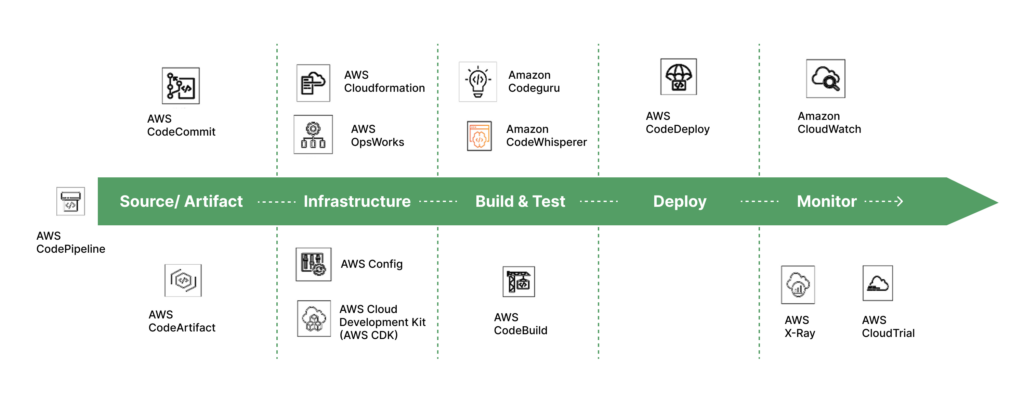
Figure 3: Sample toolchain using AWS services
Measure effectiveness of automation
Measuring the effectiveness of automation can be a complex task due to the diverse objectives of automation and the ability to measure key metrics. However, it is essential to ensure that the outcomes of the automation efforts are measured. By tracking the right metrics and using the data to make informed decisions, organizations can improve the effectiveness of automation and achieve the desired results. Here are some common metrics that are used to measure automation effectiveness:
- Cost Savings: Measure cost savings by reducing manual effort, increasing productivity, and optimizing resource utilization. Include factors such as labor costs, infrastructure costs, and operational expenses.
- Time Savings: Measure the reduction in time taken to complete specific tasks or processes, such as environment provisioning, code development, testing, or deployments.
- Defect Rate: Improved accuracy due to minimized human intervention Measure the reduction in defects that occur due to manual processes.
- Productivity: Measure the improved productivity achieved due to automation. Assess the number of tasks, transactions, or operations completed within a specific time frame.
- Quality: Evaluate the improvement in quality of outputs achieved through automation. Measure factors such as adherence to standards, compliance, and customer satisfaction.
- Process Cycle Time: Measure the reduction in process cycle time as a result of automation. Calculate the time taken from the start to the end of a specific process or workflow.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculate the ROI of automation initiatives by comparing the costs incurred with the benefits gained. Consider factors such as cost savings, productivity improvements, efficiency gains, and time to market.
- In addition, DevOps metrics can be used to measure automation effectiveness.
Maturity model
Most organizations typically assess their current state of automation using maturity models. Maturity models are good guides to setting automation goals, formulating an automation roadmap, and prioritizing automation investments. Organizations generally tailor maturity models to align with their specific needs.
Below is a model (Figure 4) that can be used to assess automation maturity in the cloud.
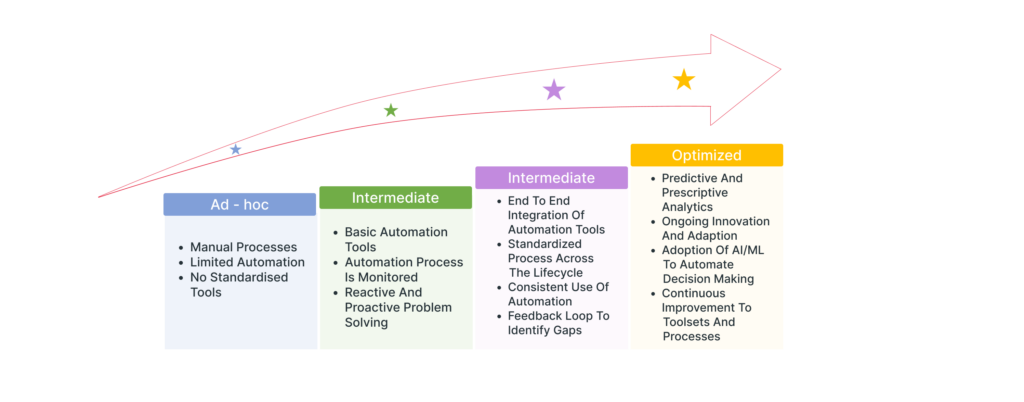
Figure 4: Maturity model
Automation metrics and maturity models are used in conjunction with each other. For each maturity level, define the specific metrics that will be used along with quantitative threshold ranges. Conduct regular audits to validate the maturity level of automation. allowing teams to measure the overall effectiveness of automation, which in turn helps to identify improvements and prioritize automation goals.
AI in automation
With the maturity of AI and ML tools and the advent of Generative AI, a whole realm of possibilities has emerged in terms of automation. AI capabilities can be used to enable automation systems to provide intelligent insights, predictive maintenance, automated incident response, and self-healing.
With Generative AI, automation can be taken to the next level by adding intelligence and flexibility to decision-making, transforming processes that were previously considered too complex for automation. Some examples of how Generative AI can be applied to automation are documentation, script and code generation, compliance reports, identification and fixing of security gaps, and automated incident responses.
AI in automation is an evolving capability, with new use cases and opportunities being identified on a regular basis. Using AI, organizations will be able to traverse through the maturity model in an accelerated fashion, driving business value faster.
Risks and challenges
While automation offers compelling benefits, it also has risks and challenges. Automation can amplify the impact of misconfigurations; over-reliance on automation can result in reduced human oversight, causing failures and unintended outcomes. Complex automation implementations cause unwieldy solutions that are difficult to maintain and drain the IT budget.
To mitigate these risks, organizations need to define their automation strategy based on a deliberate and well-thought-out approach. Conduct regular audits of the automation process, including monitoring and testing. Keep the automation process up-to-date based on changes in the landscape. Finally, in the event that automation fails, implement manual processes. Maintaining a balance between automation and its corresponding risks is important to derive the requisite benefits from automation.
In Summary
Automation greatly enhances the productivity, efficiency, and reliability of the development lifecycle and thus empowers teams to focus on innovation and value delivery. Consider automation as a strategic deliverable with key milestones defined and measured against the automation maturity model. Automation is a journey that requires attention from project initiation through implementation. Approach modernization with the mental model that automation is a deliverable by itself and is a key enabler for the program.
- Hybrid Optimization Strategies
Nutanix Cloud Clusters on AWS
Nutanix Cloud Clusters (NC2) on AWS allows you to run virtualized workloads on Nutanix’s Acropolis Hypervisor (AHV) directly on AWS infrastructure. This solution provides a seamless path to hybrid cloud by delivering the same Nutanix technologies and services across on-premises data centers and the AWS cloud. NC2 provides hybrid cloud simplicity by extending your on-premises workloads to AWS without major refactoring efforts or code changes to your apps.
By running the complete Nutanix stack natively on AWS, NC2 delivers one-click simplicity, unified management, and cloud-native integration for hybrid cloud.
NC2 on AWS is ideally suited for the following key use cases:
- Hybrid-Cloud: Utilize a single pane of glass to operate and manage your virtual machine workloads in your on-premises data center and NC2 on AWS environments.
- Migrate and Modernize Applications with AWS: Accelerate migration to AWS by relocating virtualized workloads without refactoring or rewriting applications. Quickly get on-premises workloads to AWS virtualization and modernize applications with direct AWS service integrations.
- Disaster Recovery to AWS: Configure NC2 on AWS for data replication to quickly recover business-critical workloads in a disaster recovery event. Leverage AWS’ global presence and elasticity for an Elastic DR configuration, expanding the pilot light cluster on-demand to save DR costs.
- Capacity Bursting: Instead of waiting weeks or months to purchase infrastructure, rack and stack, then operationalize hardware. You can simply consume NC2 capacity when needed and give it back when you

Hybrid capabilities with AWS services
- AWS Outposts is a family of fully managed solutions delivering AWS infrastructure and services to virtually any on-premises or edge location for a truly consistent hybrid experience. Outposts solutions allow you to extend and run native AWS services on premises, and is available in a variety of form factors, from 1U and 2U Outposts servers to 42U Outposts racks, and multiple rack deployments.
With AWS Outposts, you can run some AWS services locally and connect to a broad range of services available in the local AWS Region. Run applications and workloads on premises using familiar AWS services, tools, and APIs. Outposts supports workloads and devices requiring low latency access to on-premises systems, local data processing, data residency, and application migration with local system interdependencies.
- Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) Anywhere is a feature of Amazon ECS that lets you run and manage container workloads on your infrastructure. This feature helps you meet compliance requirements and scale your business without sacrificing your on-premises investments. Amazon ECS Anywhere provides support for registering an external instance such as an on-premises server or virtual machine (VM), to your Amazon ECS cluster. External instances are optimized for running applications that generate outbound traffic or process data. If your application requires inbound traffic, the lack of Elastic Load Balancing support makes running these workloads less efficient.
- Amazon EKS Anywhere is container management software built by AWS that makes it easier to run and manage Kubernetes on-premises and at the edge. Amazon EKS Anywhere is built on Amazon EKS Distro, which is the same reliable and secure Kubernetes distribution used by Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) in AWS Cloud.
Amazon EKS Anywhere simplifies Kubernetes cluster management through the automation of infrastructure setup and Kubernetes cluster lifecycle operations. Amazon EKS Anywhere supports different types of infrastructure including VMWare vSphere, Bare Metal, Nutanix, Apache CloudStack, and AWS Snow.
- AWS Storage Gateway is a hybrid cloud storage service that connects on-premises environments with AWS cloud storage. It allows you to seamlessly integrate your existing on-premises infrastructure with AWS, enabling you to store and retrieve data from the cloud and run applications in a hybrid environment.
Nutanix Cloud Clusters on Azure
Nutanix Cloud Clusters (NC2) on Microsoft Azure provides a hybrid cloud solution that operates as a single cloud, allowing you to manage applications and infrastructure in your private cloud and Azure. With NC2 running on Azure, you can seamlessly move your applications between on-premises and Azure using a single management console. With NC2 on Azure, you can use your existing Azure accounts and networking setup (VPN, VNets, and Subnets), eliminating the need to manage any complex network overlays. With this hybrid offering, you use the same Nutanix software and licenses across your on-premises cluster and Azure to optimize your IT investment efficiently.
You use the NC2 console to create a cluster, update the cluster capacity (the number of nodes), and delete a Nutanix cluster. After you create a Nutanix cluster in Azure using NC2, you can operate the cluster in the same manner as you operate your on-premises Nutanix cluster with minor changes in the Nutanix command-line interface (nCLI), Prism Element and Prism Central web consoles, and APIs.
NC2 runs Nutanix Acropolis Operating System (AOS) and Nutanix Acropolis Hypervisor (AHV).
- AHV hypervisor is based upon open source Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM).
- AHV will determine the lowest processor generation in the cluster and constrain all Quick Emulator (QEMU) domains to that level.
This functionality allows mixing of processor generations within an AHV cluster and ensures the ability to live-migrate between hosts.
AOS abstracts kvm, virsh, qemu, libvirt, and iSCSI from the end-user and handles all backend configuration. Thus users can use Prism to manage everything they would want to manage, while not needing to be concerned with low-level management.
Hybrid capabilities with Azure services in Azure Local
On-premises Azure Local solution integrates with Azure cloud via several cloud service components, such as Azure Local cloud service, Azure Arc, and other Azure hybrid services.
The Azure Local cloud service in Azure is a key part of the Azure Local product offering. It includes standard Azure components, such as a resource provider in Azure Resource Manager and a UI extension in the Azure portal. These components enable access to Azure Local functionality via familiar Azure tools and UX, such as Azure portal, Azure PowerShell, and Azure CLI. The Azure Local cloud service also enables contextual navigation from an Azure Local resource to its Arc-enabled servers and Azure Local virtual machines (VMs) enabled by Azure Arc.
Hybrid Cloud storage
Hybrid cloud storage is a versatile data management strategy that combines on-premises and cloud-based infrastructure. Think of it as a tailored solution, where your sensitive, critical data resides securely on your own servers, enjoying the comforts of a private sanctuary, while your more flexible, dynamic data is relegated to the public cloud. This approach helps organizations optimize their storage resources, scaling data capacities on demand to meet varying needs.
The real beauty of hybrid cloud storage lies in its adaptability. As you navigate the space between on-premises and the cloud, you can strategically position your data based on performance, cost, and security considerations. This allows you to straddle both worlds, seamlessly enjoying the benefits of each through a unified platform. Ultimately, this approach provides both a cohesive storage solution and an effective balance between flexibility and security.
4. Security, Governance & Compliance Optimization
In an on-premises environment, security governance relies on the periodic data that’s available about the environment. This approach often results in outdated information. Cloud technology revolutionizes this process by providing on-demand visibility into the current security posture and asset coverage. This real-time insight transforms governance into a more dynamic organization. It fosters closer collaboration with other security teams to monitor security standards, provide guidance, and enhance processes.
In its ideal state, governance drives continuous improvement throughout the organization. This ongoing process engages all parts of the organization to ensure constant security advancements.
The following are key principles for security governance:
- Continuous discovery of assets and asset types: A static inventory isn’t possible in a dynamic cloud environment. Your organization must focus on the continuous discovery of assets and asset types. In the cloud, new types of services are added regularly. Workload owners dynamically adjust the number of application and service instances as needed, which creates a constantly changing environment. This situation makes inventory management a continuously evolving discipline. Governance teams need to continuously identify asset types and instances to keep up with this pace of change.
- Continuous improvement of asset security posture: Governance teams should focus on improving and enforcing standards to keep up with the cloud and attackers. Information technology (IT) organizations must react quickly to new threats and adapt accordingly. Attackers constantly evolve their techniques, while defenses continuously improve and might need to be updated. You can’t always incorporate all necessary security measures in the initial setup.
- Policy-driven governance: This governance ensures consistent implementation because you define policies once and apply them automatically across resources. This process limits wasted time and effort on repeated manual tasks. It’s often implemented by using Azure Policy or non-Microsoft policy automation frameworks.
To maintain agility, best practices guidance is often iterative. It digests small pieces of information from multiple sources to create the whole picture and continuously make small adjustments.
It’s critical to monitor compliance and enforce policies to maintain the principle of confidentiality in enterprise cloud environments. These actions are essential for robust security standards. These processes ensure that all security measures are consistently applied and effective to help protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and breaches. Regular assessments, automated monitoring, and comprehensive training programs are essential to ensure adherence to established policies and procedures.
- Regular audits and assessments: Conduct regular security audits and assessments to ensure that policies are being followed and identify areas for improvement. These audits should cover regulatory, industry, and organizational standards and requirements, and might involve third-party assessors to provide an unbiased evaluation. An approved assessment and inspection program helps maintain high standards of security and compliance, and ensures that all aspects of data confidentiality are thoroughly reviewed and addressed.
- Automated compliance monitoring: Tools like Azure Policy automate the monitoring of compliance with security policies and provide real-time insights and alerts. This functionality helps ensure continuous adherence to security standards. Automated monitoring helps you detect and respond to policy violations quickly, which reduces the risk of data breaches. It also ensures continuous compliance by regularly checking configurations and access controls against established policies.
- Training and awareness programs: Educate employees about data confidentiality policies and best practices to foster a security-conscious culture. Regular training sessions and awareness programs help ensure that all staff members understand their roles and responsibilities in maintaining data confidentiality. These programs should be updated regularly to reflect changes in policies and emerging threats. This strategy ensures that employees are always equipped with the latest knowledge and skills.

